🗣️ Let’s Talk—What Are You Seeing?
📩 Reply to this email or drop a comment.
🔗 Not subscribed yet? It is only a click away.
In "This Week in Disinformation," we're peeling back the layers on how a global power fabricated stories about French Rafale jets, exposing how diplomatic pressure combined with online fakes sought to undermine critical defence sales.
We then reveal how a fast-fashion giant got busted for a staggering €40 million in deceptive pricing in France, with over half its "discounts" offering no real savings.
Finally, we examine how a social media titan is marking a critical shift towards hybrid human-AI content moderation models. It's a deep dive into the deliberate deceptions shaping our world, and how to spot them.
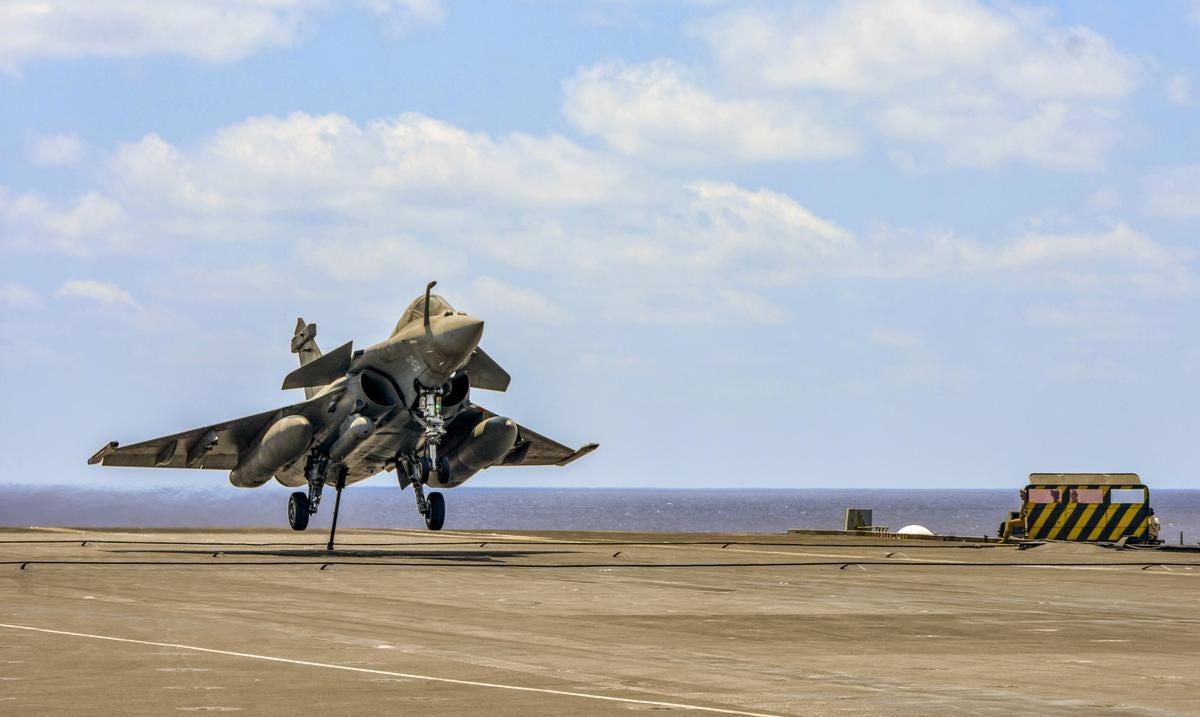
Beijing's Disinformation Campaign Targets French Rafale Jet Sales
◾ 1. Context
The global arms market is a difficult race where countries fight for power and money through selling weapons.
France relies on its defence industry, particularly the export of its Rafale fighter jets, to strengthen international ties and maintain strategic autonomy. Against this backdrop, China seeks to expand its regional dominance, particularly in Asia.
The competitive landscape between French and Chinese defence exports intensified following the India-Pakistan aerial clashes in May. There, Indian Air Force Rafales saw combat.
◾ 2. What Happened
French intelligence found that China executed a major disinformation campaign against the French Rafale jet.
This campaign emerged after the Rafale's combat involvement in the India-Pakistan clashes in May.
Chinese defence attaches in foreign embassies actively lobbied officials in countries that had purchased or were considering purchasing Rafales, such as Indonesia. Chinese officials argue that the Indian Air Force Rafales performed poorly and simultaneously promoting Chinese-made aircraft.
At the same time, over 1,000 new social media accounts spread fake stories, strongly suggesting coordination. These included viral posts, faked images of Rafale wreckage, computer-made content, and video game clips pretending to be real combat.
This all aimed to widely spread the idea that Chinese technology was better.
◾ 3. Nature of Information
The information disseminated during this campaign is classified primarily as Disinformation, with elements of Malinformation and Factual information used out of context.
The core claims that Indian Air Force Rafales performed poorly or were shot down is false. It is designed to deceive potential buyers and undermine confidence in French military technology.
The intent behind the spread was clearly to damage the Rafale's reputation, deter further sales, and encourage the adoption of Chinese-made military aircraft.
◾ 4. Character of Information
The campaign used various methods such as, combining official talks with online tactics, all revealing the nature of information warfare.
Chinese defence officials met directly with leaders in target countries like Indonesia. Online, they used social media sites like X, Instagram, Facebook, and TikTok.
One notable action was a fake story about a "Muslim heroine". This was a Pakistani pilot who supposedly shot down Rafales with a Chinese jet. This story was culturally appealing in Indonesia. More than 1,000 new social media accounts spread Chinese superiority claims.
The false claim that Indonesia suspended its Rafale purchase, circulated by a Russian-linked site, is a hoax.
The hashtag #HentikanRafaleDeal on X showed signs of being boosted falsely, meaning it looked popular but wasn't real. Early Indonesian posts were just translations of Chinese content, spread by Chinese-Indonesian influencers, showing a clear plan to localize the lies.
◾ 5. Impact & Information Effects Statement
It is assessed with High confidence that China’s multi-pronged dissemination of false narratives regarding Rafale jet performance has generated significant online traction and public exposure to deceptive claims.
This was likely intended to undermine French defence exports, weaken its strategic partnerships, and promote Chinese military alternatives.
◾ 6. Strategic Implications And Lessons Learnt
This incident clearly demonstrates that modern geopolitical competition increasingly relies on hybrid threats, seamlessly blending overt diplomatic pressure with covert online disinformation to achieve both strategic and commercial objectives.
The sophisticated integration of state-backed lobbying with advanced digital manipulation marks a significant evolution in influence operations.
Rather than directly attacking military assets, these campaigns target a nation's "strategic autonomy, industrial reliability, and solid partnerships".
Sources:
China Used Embassies To Undermine Rafale Sales After India-Pakistan Tensions: Report
French intelligence: China used embassies to undermine sales of... - RiverBender.com
'To discourage buyers': How China used its embassies to undermine... - Times of India
Indonesia targeted in Rafale fighter jet disinformation | Lowy Institute
Shein Disinformation In France
◾ 1. Context
Shein operates as a dominant force in the ultra-fast fashion industry. It is characterized by its rapid production cycles, low prices, and extensive digital presence.
This aggressive market penetration is supported by a sophisticated digital strategy that includes partnerships with micro-influencers. It offers complimentary products and high commission rates on referral sales.
◾ 2. What Happened
France's antitrust authority, the Directorate-General for Competition, Consumer Affairs and Fraud Control (DGCCRF), imposed a substantial fine on Shein for misleading promotional practices and unsubstantiated environmental claims.
On July 3, 2025, the regulator announced a €40 million fine (equivalent to $47 million) on Infinite Style E-commerce Ltd (ISEL), the entity responsible for Shein's sales in France.
An investigation, conducted between October 2022 and August 2023, revealed that over half (57%) of Shein's announced price reductions offered no real discount, 19% provided a smaller reduction than advertised, and 11% were actually price increases.
Furthermore, Shein was unable to verify its claims of reducing greenhouse gas emissions by 25%.
Essentially, Shein was caught lying on a huge scale.
◾ 3. Nature of Information
The information disseminated by Shein, particularly concerning its pricing and environmental claims, is classified as disinformation.
This categorization is based on the findings of the French antitrust authority, which concluded that Shein intentionally presented false information to deceive consumers about the reality of price reductions and its environmental impact.
The company's use of a "digital army of fake commentators and bots" to post repetitive promotional messages and defend the brand against criticism also falls under disinformation. These are fabricated narratives designed to manipulate public perception with the intent to drive sales.
◾ 4. Character of Information
Shein's information dissemination strategy leverages a multi-faceted approach across various digital platforms, primarily its own website and popular social media channels like Instagram, YouTube, and TikTok.
One prominent manipulation strategy involves deceptive pricing and "dark patterns." The French investigation found that Shein manipulated price reductions, with a significant majority of promotions offering no real discount or even price increases.
This confirms the intent of Shein of misleading its customers.
Another key tactic is astroturfing and the deployment of a "digital army of fake commentators and bots." These accounts post repetitive promotional messages, such as "I'm shocked the Shein promo code in your bio really worked!", and frequently share positive product reviews.
◾ 5. Impact & Information Effects Statement
It is assessed with High confidence that Shein’s dissemination of misleading promotional claims and astroturfed positive narratives has eroded consumer trust and prompted significant regulatory intervention on consumer protection and environmental claims.
This was likely intended to maximize sales and mitigate reputational damage.
◾ 6. Strategic Implications And Lessons Learnt
The public should remain alert to the increasing sophistication of AI-generated content used for astroturfing, the pervasive use of "dark patterns" in e-commerce, and the continuous blurring of lines between genuine user-generated content and paid promotion.
Geopolitically, France's selective targeting of Chinese ultra-fast fashion brands like Shein and Temu, while largely sparing European giants such as Zara and H&M, suggests a strategic move to protect domestic industries and assert digital sovereignty.
Sources
The Independent Influencers face backlash for promoting Shein factory during PR trip in China
ICLG France slaps SHEIN with EUR 40 million fine over misleading practices
Fashion Dive Shein fined $47M for misleading promotions in France
Daxue Consulting Viral success, ethical controversy: Dissecting Shein’s marketing strategy
Moades France vs. Shein: €40M Fine Issued for Unfair Commercial Practices
X Brings AI into Community Notes to Fight Misinformation at Scale Humans Can’t Match
◾ 1. Context
X's Community Notes, launched in 2021, aimed to crowdsource fact-checking, but faced limitations like slow publication times and difficulty achieving cross-ideological consensus.
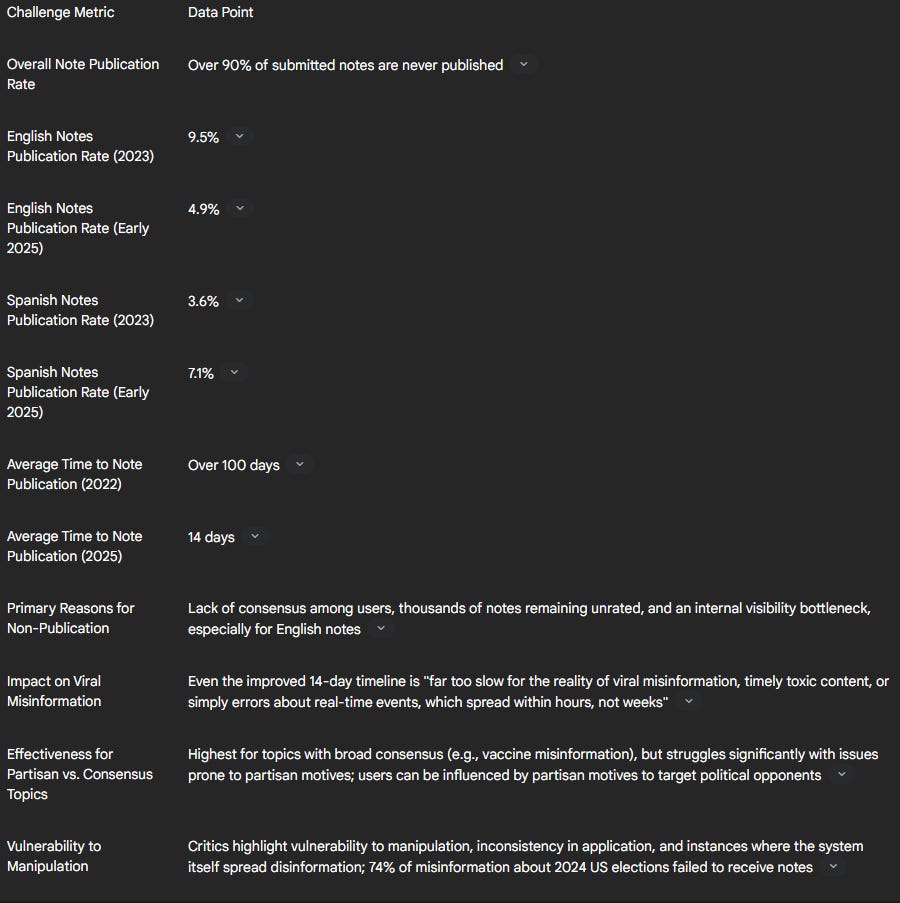
Over 90% of submitted notes remained unpublished. Even published notes took an average of 14 days to appear, too slow for viral content. X's intent is to overcome these bottlenecks and enhance its ability to provide context to misleading posts.
The table shows the key challenges and publication rates of community notes pre-AI assisted.
◾ 2. What Happened
On July 3, 2025, X launched a pilot program integrating Artificial Intelligence (AI) into Community Notes.
This initiative allows large language models, including X's Grok, to act as "AI Note Writers" and propose contextual notes for public posts.
These AI-generated notes must still undergo the same human peer-review process, requiring cross-ideological consensus before publication. X aims for AI to boost the program's speed and scale, while also improving accuracy and reducing bias in content moderation
◾ 3. Nature of Information
The information regarding X's integration of AI into Community Notes is Factual. This initiative represents a strategic move by X to enhance its content moderation capabilities.
The intent behind this development is to improve the efficiency and scalability of fact-checking on the platform, directly addressing the challenges posed by the rapid spread of misinformation.
◾ 4. Character of Information
X's AI integration involves deploying large language models, such as Grok, as "AI Note Writers" to generate proposed notes.
These AI contributions are then subjected to the existing human peer-review process, which requires agreement from diverse perspectives for a note to be published.
This hybrid approach aims to leverage AI's speed and volume capabilities while maintaining human oversight for accuracy and nuance. All AI-written notes will be clearly marked for users to ensure transparency
◾ 5. Impact & Information Effects Statement
It is assessed with High confidence that X's integration of AI into Community Notes has the potential to significantly enhance the platform's ability to combat misinformation at scale.
This is likely intended to improve content moderation efficiency, user trust, and platform integrity on the basis of the quality of moderation.
However, the nature of the AI to power this is still in question.
◾ 6. Strategic Implications And Lessons Learnt
This move signifies a critical shift towards hybrid AI-human content moderation models, acknowledging that the scale of online misinformation now demands technological solutions beyond human capacity alone. It highlights an escalating "AI vs. AI" arms race, where generative AI creates sophisticated falsehoods, requiring equally advanced AI detection tools.